Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. Therefore, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. The origin of the term “carbohydrate” is based on its components: carbon (“carbo”) and water (“hydrate”).
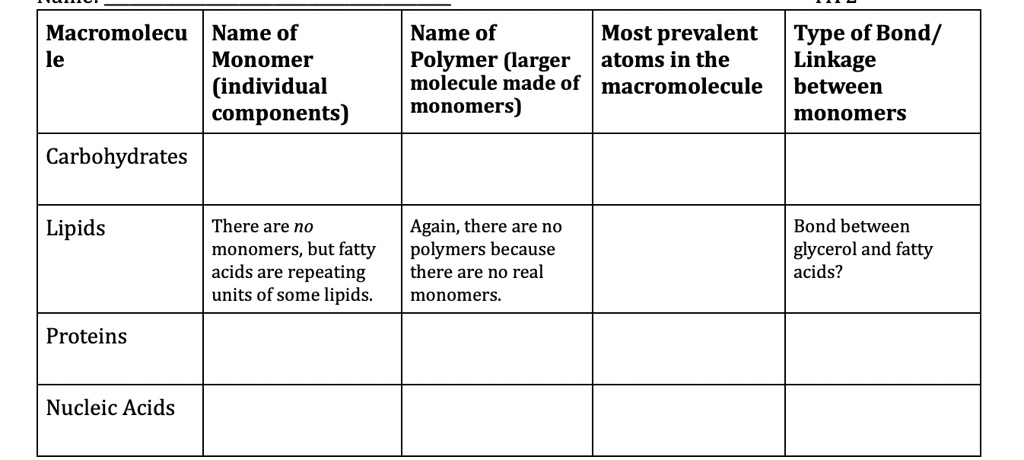
SOLVED: Macromolecule Name of the Monomer (individual components) Name of the Most Prevalent Type of Bond/ Polymer (larger atoms in the molecule made of macromolecule between monomers) monomers Carbohydrates Lipids There are
The differences between them is the linkage between the glucose monomers. In starch and glycogen, which are energy storage polysaccharides, the linkage is alpha 1-4. In cellulose, the most abundant biomolecule, the linkage is beta 1-4. The beta linkage ensures that all bulky groups on the glucose chairs are in the more stable, equatorial position.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
In sucrose, a glycosidic linkage is formed between carbon 1 in glucose and carbon 2 in fructose. Common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose (Figure 3.2.5 3.2. 5 ). Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the monomers glucose and galactose. It is found naturally in milk.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Connecting Macromolecule Type to Function Practice | Biology Practice Problems | Study.com
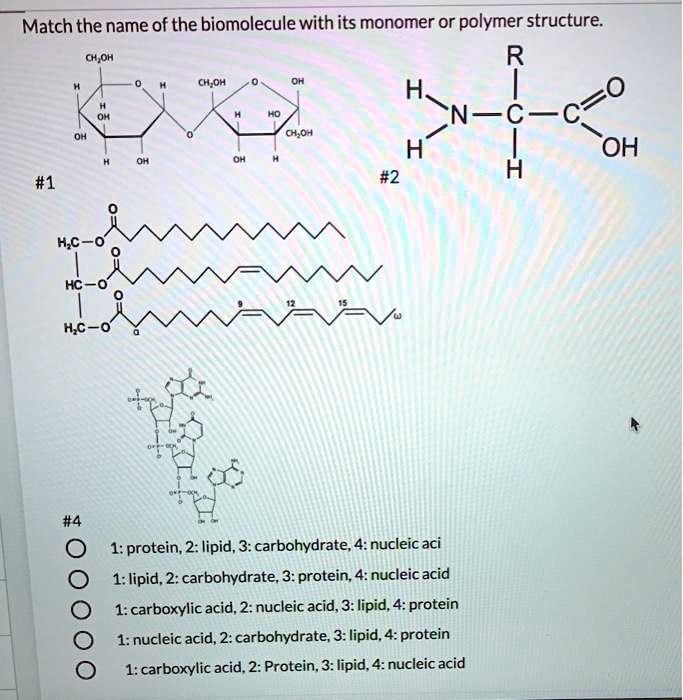
For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 114 votes) Show more

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
What Is The Monomer Of A Carbohydrate Called
For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 114 votes) Show more
Sep 21, 2023Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes, polyhydroxy ketones, or other compounds that hydrolyze to polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones. The general formula of simple carbohydrates is CnH2nOn C n H 2 n O n, which can also be written as Cn ⋅ (H2O)n C n ⋅ ( H 2 O) n which is the origin of the name carbohydrates, i.e., hydrates of carbon.
Bond Linking Monomers: Types with Concepts, Videos and Examples
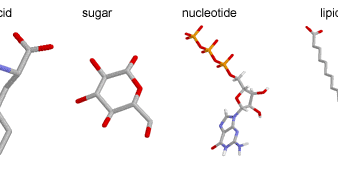
Glycosidic bonds (also called glycosidic linkages) can be of the alpha or the beta type. Figure 4. Sucrose is formed when a monomer of glucose and a monomer of fructose are joined in a dehydration reaction to form a glycosidic bond. In the process, a water molecule is lost. By convention, the carbon atoms in a monosaccharide are numbered from
What are the monomers of carbohydrates? – Quora
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Biology Notes for A level: #16 Summary of Biological Molecules
Glycosidic bonds (also called glycosidic linkages) can be of the alpha or the beta type. Figure 4. Sucrose is formed when a monomer of glucose and a monomer of fructose are joined in a dehydration reaction to form a glycosidic bond. In the process, a water molecule is lost. By convention, the carbon atoms in a monosaccharide are numbered from
Source Image: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Macromolecule Name of the Monomer (individual components) Name of the Most Prevalent Type of Bond/ Polymer (larger atoms in the molecule made of macromolecule between monomers) monomers Carbohydrates Lipids There are
Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. Therefore, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. The origin of the term “carbohydrate” is based on its components: carbon (“carbo”) and water (“hydrate”).
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Connecting Macromolecule Type to Function Practice | Biology Practice Problems | Study.com
In sucrose, a glycosidic linkage is formed between carbon 1 in glucose and carbon 2 in fructose. Common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose (Figure 3.2.5 3.2. 5 ). Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the monomers glucose and galactose. It is found naturally in milk.

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
concept 3 Flashcards | Quizlet
Jan 2, 2024carbohydrate, class of naturally occurring compounds and derivatives formed from them. In the early part of the 19th century, substances such as wood, starch, and linen were found to be composed mainly of molecules containing atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and to have the general formula C 6 H 12 O 6; other organic molecules

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
420+ Carbohydrate Molecule Stock Illustrations, Royalty-Free Vector Graphics & Clip Art – iStock | Glucose molecule, Carbohydrate structure, Protein molecule
For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 114 votes) Show more
Source Image: istockphoto.com
Download Image
What are Carbohydrates? (Review Video)
Sep 21, 2023Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes, polyhydroxy ketones, or other compounds that hydrolyze to polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones. The general formula of simple carbohydrates is CnH2nOn C n H 2 n O n, which can also be written as Cn ⋅ (H2O)n C n ⋅ ( H 2 O) n which is the origin of the name carbohydrates, i.e., hydrates of carbon.

Source Image: mometrix.com
Download Image
Biology Notes for A level: #16 Summary of Biological Molecules
What are Carbohydrates? (Review Video)
The differences between them is the linkage between the glucose monomers. In starch and glycogen, which are energy storage polysaccharides, the linkage is alpha 1-4. In cellulose, the most abundant biomolecule, the linkage is beta 1-4. The beta linkage ensures that all bulky groups on the glucose chairs are in the more stable, equatorial position.
Connecting Macromolecule Type to Function Practice | Biology Practice Problems | Study.com 420+ Carbohydrate Molecule Stock Illustrations, Royalty-Free Vector Graphics & Clip Art – iStock | Glucose molecule, Carbohydrate structure, Protein molecule
Jan 2, 2024carbohydrate, class of naturally occurring compounds and derivatives formed from them. In the early part of the 19th century, substances such as wood, starch, and linen were found to be composed mainly of molecules containing atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and to have the general formula C 6 H 12 O 6; other organic molecules